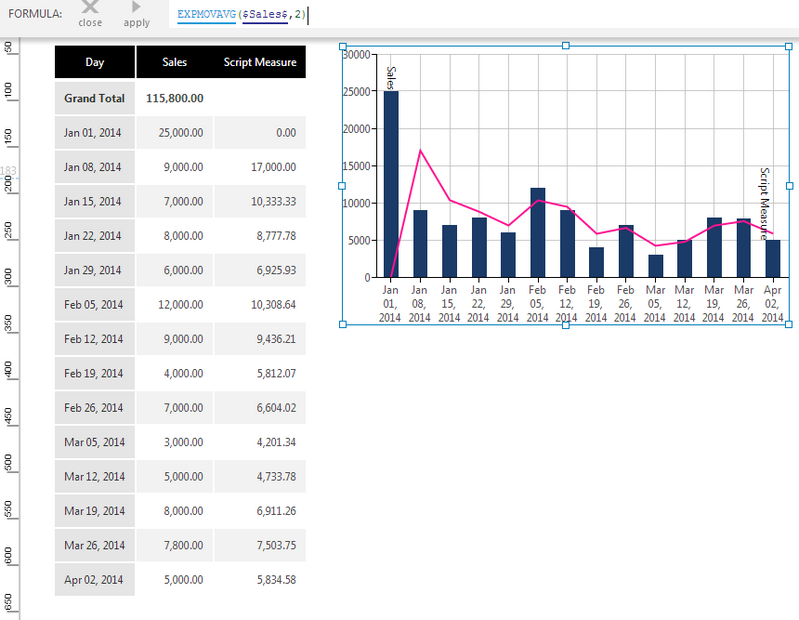
Exponential Moving Average
The Exponential Moving Average, or exponentially weighted moving average (EWMA), function computes the average of a set of input values over a specified number of periods. In this function, a greater weight is given to more recent data. This function can be used to smooth a data series, which helps to reduce noise and make it easier to spot data trends.
The mathematical formula being calculated is as follows:
EWMAt = λYt + (1 – λ)EWMAt-1
for t = 1, 2, ..., n.
Where EWMA0 is the mean of historical data, Y is the value, n is the number of periods, and λ is the weight constant, which is set to 2 / (n +1). You can find more information from the National Institute of Standards and Technology.
1. Syntax
EXPMOVAVG(d0,s0,Alignment)
2. Input
The Exponential Moving Average function requires the following input:
- d0 - The set of data values for which the Exponential Moving Average is calculated.
3. Parameters
The Exponential Moving Average function requires the following parameters:
- s0 - The number of periods to use in the calculation. The default value is 10.
- Alignment (Optional) – Hierarchy placeholder to be used as the alignment axis.
4. Output
The Exponential Moving Average function generates the following output:
- Exponential Moving Average - The Exponential Moving Average result set.