Join
The Join transform combines two separate tables together by matching up their rows. All of the columns from both tables can be included.
If the data connector of the transforms being joined are the same, and that provider supports joining, the joining can be automatically included as part of the query sent to the database if no preceding transform is added that must be run directly.
1. Input
The Join transform requires two input transforms.
2. Configure
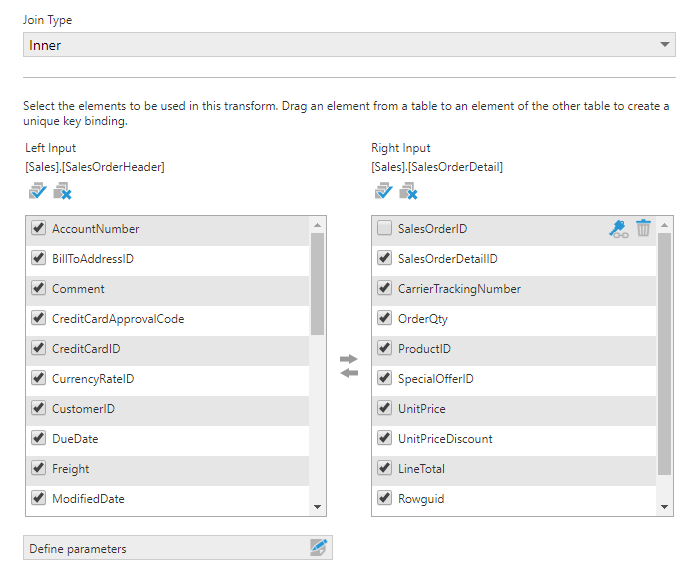
The Join configuration dialog lists the columns of the two input tables, and includes settings to determine how they are joined.
Choose the Join Type to determine which records should be included:
- Inner Join - Only records with matching key values in both input tables.
- Left Join - Only records with a key value in Left Input.
- Right Join - Only records with a key value in Right Input.
- Full Join - All original records will be included.
A join requires you to designate one or more columns as keys in each table. Rows from the two tables with matching key values will be combined into a single row.
If a relationship between the two tables was already defined, the key elements may have already been set. This will be indicated by a key icon shown next to one or more items in each list, like in the figure above. If you want to remove an existing key binding for your join, click the Delete icon next to the key icon.
To define a key binding, drag a column from one input table and drop it onto the corresponding column in the other input table.
- Use the checkboxes to select or de-select columns for inclusion in the output. For example, you might choose to de-select a column in one list that contains the same values as another column already selected.
3. Output
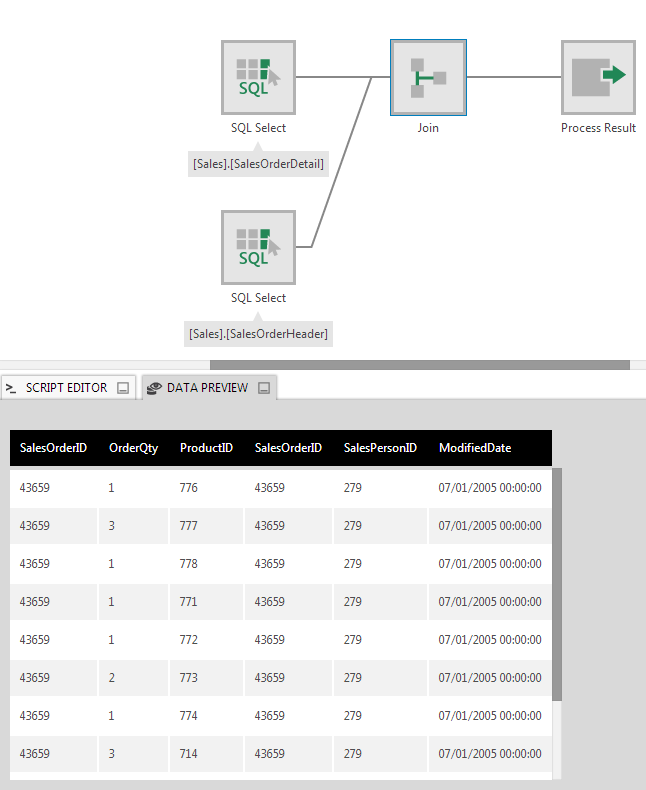
The figure below illustrates the output of a join between two tables that each contained a SalesOrderID column used as the key values.