Dundas BI Linux services
1. Overview
This article describes the Dundas BI services that run on Linux servers and how to control them. You can use this article for reference after installing Dundas BI on Linux.
2. Using systemd to control Dundas BI services
systemd is a system and service manager for Linux. All Dundas BI services that are created with the instance exist as systemd services.
When you create an instance, the following services are created:
| Service | Description | Service Definition Path |
|---|---|---|
| Dundas BI website | The Dundas BI website service runs the .NET Core Kestrel website for Dundas BI. |
/etc/systemd/system/dundas-bi-website-{InstanceName}.service
|
| Dundas BI AuthBridge website | The Dundas BI AuthBridge service runs the .NET Core Kestrel website for Dundas BI federated authentication. |
/etc/systemd/system/dundas-bi-authbridge-{InstanceName}.service
|
| Dundas BI scheduler | The Dundas BI scheduler service runs the .NET Core scheduler for Dundas BI. |
/etc/systemd/system/dundas-bi-scheduler-{InstanceName}.service
|
| Dundas BI X Virtual Frame Buffer service | The Dundas BI X Virtual Frame Buffer service is used to create images during export. |
/etc/systemd/system/dundas-bi-xvirtualframebuffer.service |
2.1. Commands to control Dundas BI services
2.1.1. Dundas BI website commands
The following table gives typical commands for controlling the website service:
| Command | Result |
|---|---|
systemctl stop dundas-bi-website-{InstanceName}.service
|
Stops the Dundas BI Kestrel website. |
systemctl start dundas-bi-website-{InstanceName}.service
|
Starts the Dundas BI Kestrel website. |
systemctl restart dundas-bi-website-{InstanceName}.service
|
Restarts the Dundas BI Kestrel website. |
systemctl status dundas-bi-website-{InstanceName}.service
|
Get the Dundas BI Kestrel website status. |
2.1.2. Dundas BI AuthBridge commands
The following table gives typical commands for controlling the AuthBridge website service:
| Command | Result |
|---|---|
systemctl stop dundas-bi-authbridge-{InstanceName}.service
|
Stops the Dundas BI AuthBridge Kestrel website. |
systemctl start dundas-bi-authbridge-{InstanceName}.service
|
Starts the Dundas BI AuthBridge Kestrel website. |
systemctl restart dundas-bi-authbridge-{InstanceName}.service
|
Restarts the Dundas BI AuthBridge Kestrel website. |
systemctl status dundas-bi-authbridge-{InstanceName}.service
|
Get the Dundas BI AuthBridge Kestrel website status. |
2.1.3. Dundas BI scheduler commands
The following table gives typical commands for controlling the scheduler service:
| Command | Result |
|---|---|
systemctl stop dundas-bi-scheduler-{InstanceName}.service
|
Stops the Dundas BI scheduler. |
systemctl start dundas-bi-scheduler-{InstanceName}.service
|
Starts the Dundas BI scheduler. |
systemctl restart dundas-bi-scheduler-{InstanceName}.service
|
Restarts the Dundas BI scheduler. |
systemctl status dundas-bi-scheduler-{InstanceName}.service
|
Gets the Dundas BI scheduler status. |
2.1.4. Dundas BI X Virtual Frame Buffer service
The following table gives typical commands for controlling the X Virtual Frame Buffer service:
| Command | Result |
|---|---|
systemctl stop dundas-bi-xvirtualframebuffer.service |
Stops the Dundas BI X Virtual Frame Buffer Service. |
systemctl start dundas-bi-xvirtualframebuffer.service |
Starts the Dundas BI X Virtual Frame Buffer Service. |
systemctl restart dundas-bi-xvirtualframebuffer}.service |
Restarts the Dundas BI X Virtual Frame Buffer Service. |
systemctl status dundas-bi-xvirtualframebuffer.service |
Gets the Dundas BI X Virtual Frame Buffer Service status. |
3. Troubleshooting Linux services
If the Dundas BI website is not serving content when you visit its URL, the first thing to check is whether the website service is running. To do this, you would execute the following command given as an example above:
systemctl status dundas-bi-website-{InstanceName}.service
Here you are expecting to see an active status as shown below:
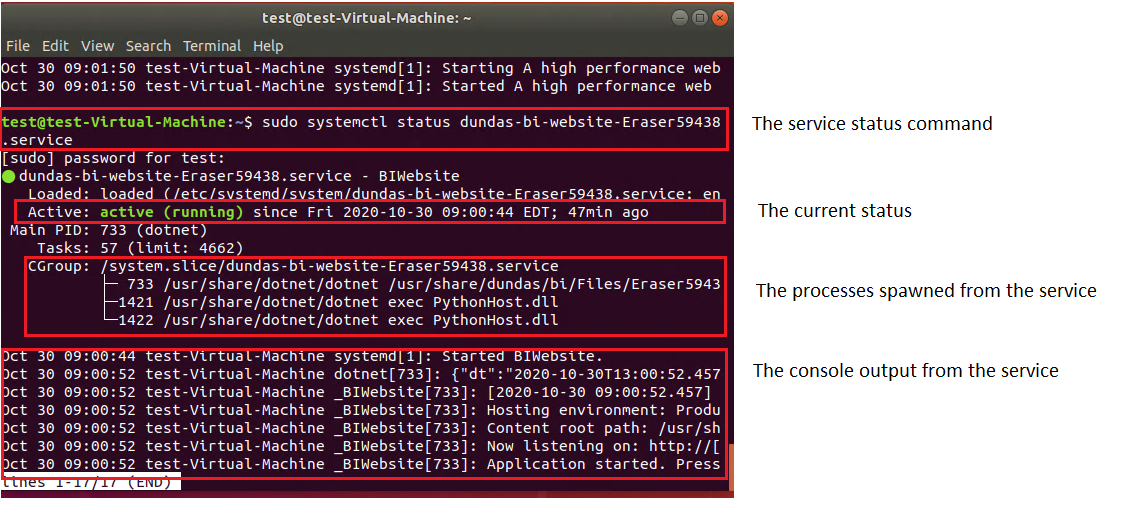
If the website seems to be running, check the reverse proxy server that you configured. As Dundas BI allows for various reverse proxies to be used, it is best to check with the documentation for the particular reverse proxy and Linux distribution you are using, such as for NGINX with SELinux on RHEL.
3.1. journalctl
If you would like to see more console logs from the Dundas BI services, you can use the journalctl command. The following example demonstrates how to get all the Dundas BI website service logs:
journalctl -u dundas-bi-website-{InstanceName}.service
