Seat types
1. Overview
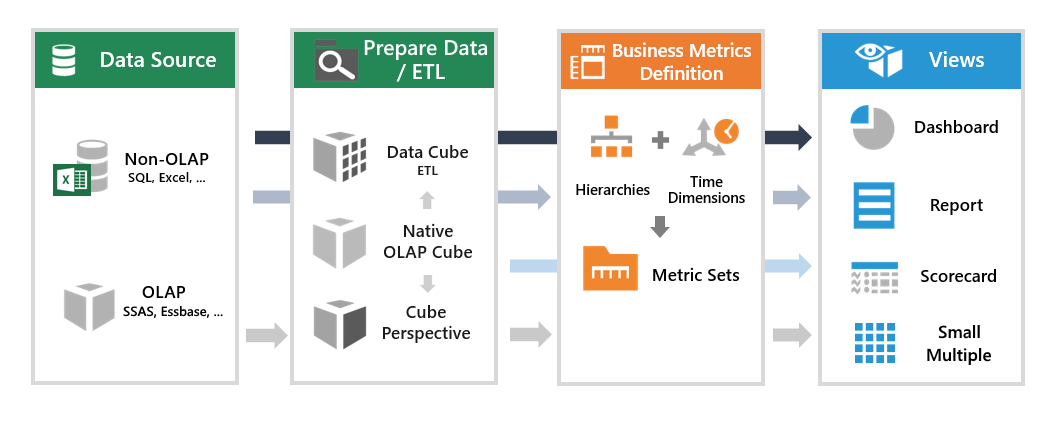
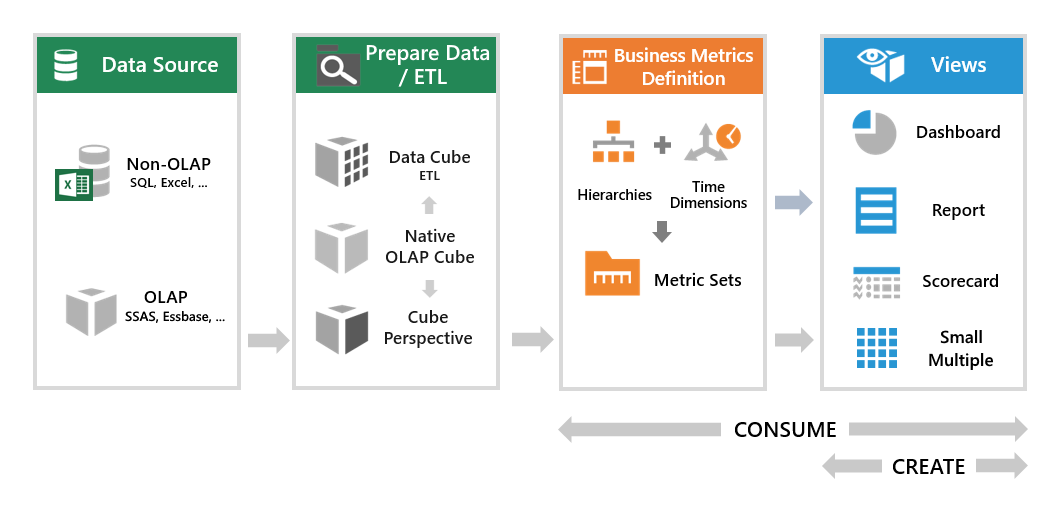
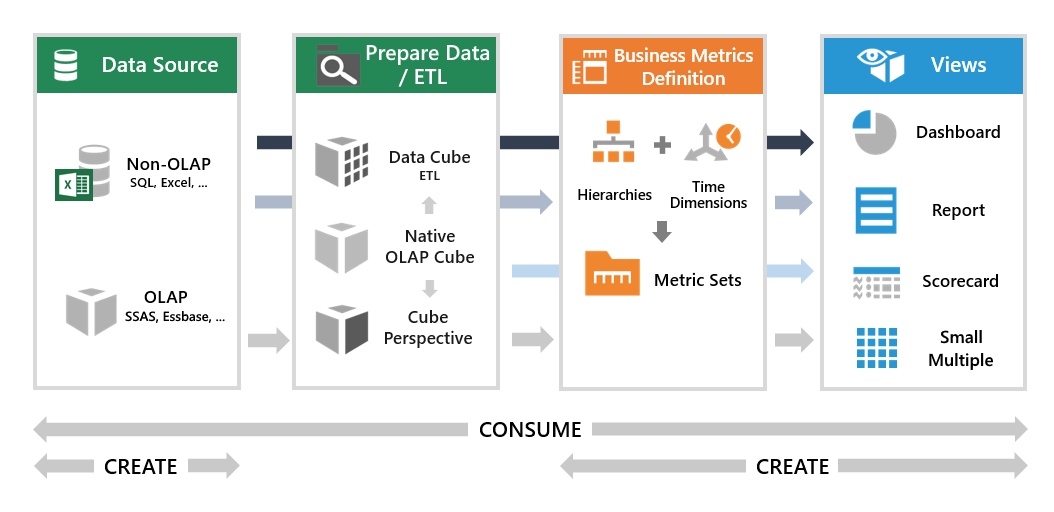
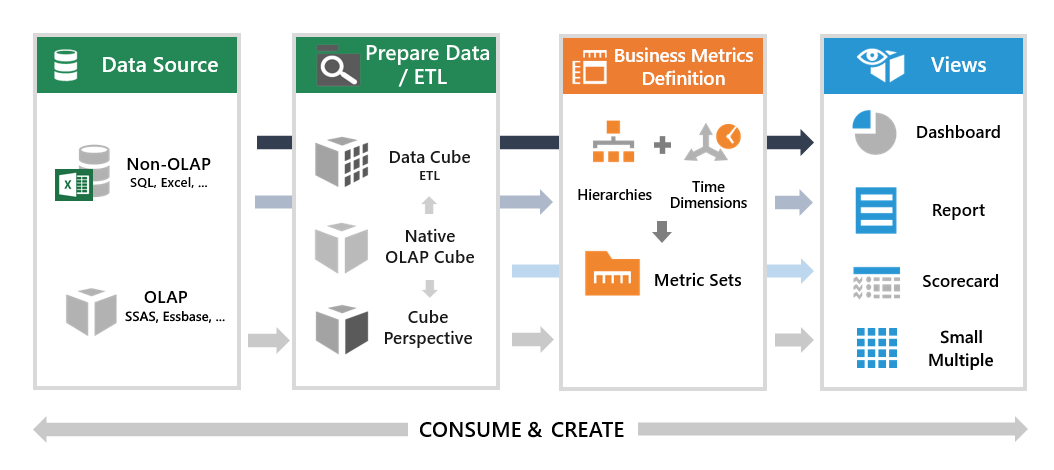
A concept of seats is used to allow users to log on, and the type of seat they are assigned determines their abilities and data access in the application. The three types of seats are integrated with our licensing model and the application data flow:
Related video: Data Flow
2. Standard User
The standard user seat is targeted at users looking to consume or explore using business metrics and content that are largely predefined. As an example, consider a business user. The user can view and interact with the dashboards that were created for him, but may also like to combine visualizations from two different dashboards into a single dashboard for his own use. He can create a dashboard in his own project, add the existing visualizations and a title, add and connect a filter, and change the font sizes.
Users with the standard user seat can:
- View and interact with existing views, such as dashboards, reports, and scorecards.
- Collaborate by sharing links or exports, posting notes to visualization data points, and setting up notifications.
- Personalize views by re-visualizing or changing appearance settings.
- Create 'mashups' combining existing business metric definitions (metric sets) or other views, and add filters, other components, and custom interactions.
3. Power User
The power user seat is targeted at users looking to analyze data with access to the full set of analysis tools. As an example, consider a business analyst who would like to visualize some particular data. She can create a new metric set based on an existing data cube model, an Excel file dragged into the application, or another data source. She can group and aggregate, get the top 10 items, add a formula, and completely customize the visualization as needed. The analyst can then share the metric set for other users to add to dashboards, or add it to a dashboard and check it in for viewing.
Users with the power user seat can:
- Connect to data sources such as Excel, databases, or other data sources (if they have access to them), and auto-join data together if needed.
- Access data from data cubes prepared for them with data cleansing, data consolidation and meta-data.
- Add formulas and period over period comparisons, apply hierarchies & time dimensions to raw data, and use other analysis tools.
- Design using the full set of properties for visualizations, components and views.
- Do everything a standard user can.
4. Developer
The developer seat is targeted at users who need to prepare the data before other users can analyze or work with it, or need access to advanced data transformation or scripting options. As an example, consider a technical Business Intelligence (BI) professional who would like to make sure users have access to data that has been prepared and approved before other users can work with it. He can combine and prepare data from the company’s databases, and make the result available for power users to use instead of the raw data.
Users with the developer seat can:
- Create and edit data cubes for performing data transformation, preparing data models with predefined meta-data, and optimizing performance using data storage.
- Write custom queries, use Python or R to generate or analyze data, or write script in dashboards or other views for advanced customization.
- Do everything a power user can.
5. Administrator
Any user can be added to the System Administrators group, regardless of their seat type. Administrator privileges do not integrate with our licensing model, and are not related to the data flow. These users can:
- Manage user accounts, groups, sessions, and projects.
- View logs and change application configuration settings.
- Manage licensing and multi-tenancy.
- Import and export content between application instances.
See the administration overview for more administration options.
As an administrator, you can assign the seat type for each user account, or for groups of users assigned floating seats.